

#PYTHON JUPYTER NOTEBOOK WITH LINKS TO OTHER NOTEBOOKS CODE#
Jupyter Notebooks, which can actually contain R and Julia code in place of Python code, have a. They are a cornerstone in efforts to promote reproducible research.Īs we’ll see soon enough, a standard Python file is simply a text file containing only Python code (and comments), and has a. They are an incredibly powerful yet simple means for sharing your work in a way that reveals both your results, sometimes as interactive visualizations, but also the exact code used to produce these results. Those of you who have worked with R-Markdown files are familiar with this concept. Starting Jupyter Notebooks What is a Jupyter Notebook?Ī Jupyter Notebook is a blend of formatted text and live code. Save and export documents in alternative formatsġ. Write and format text in a notebook’s markdown cell
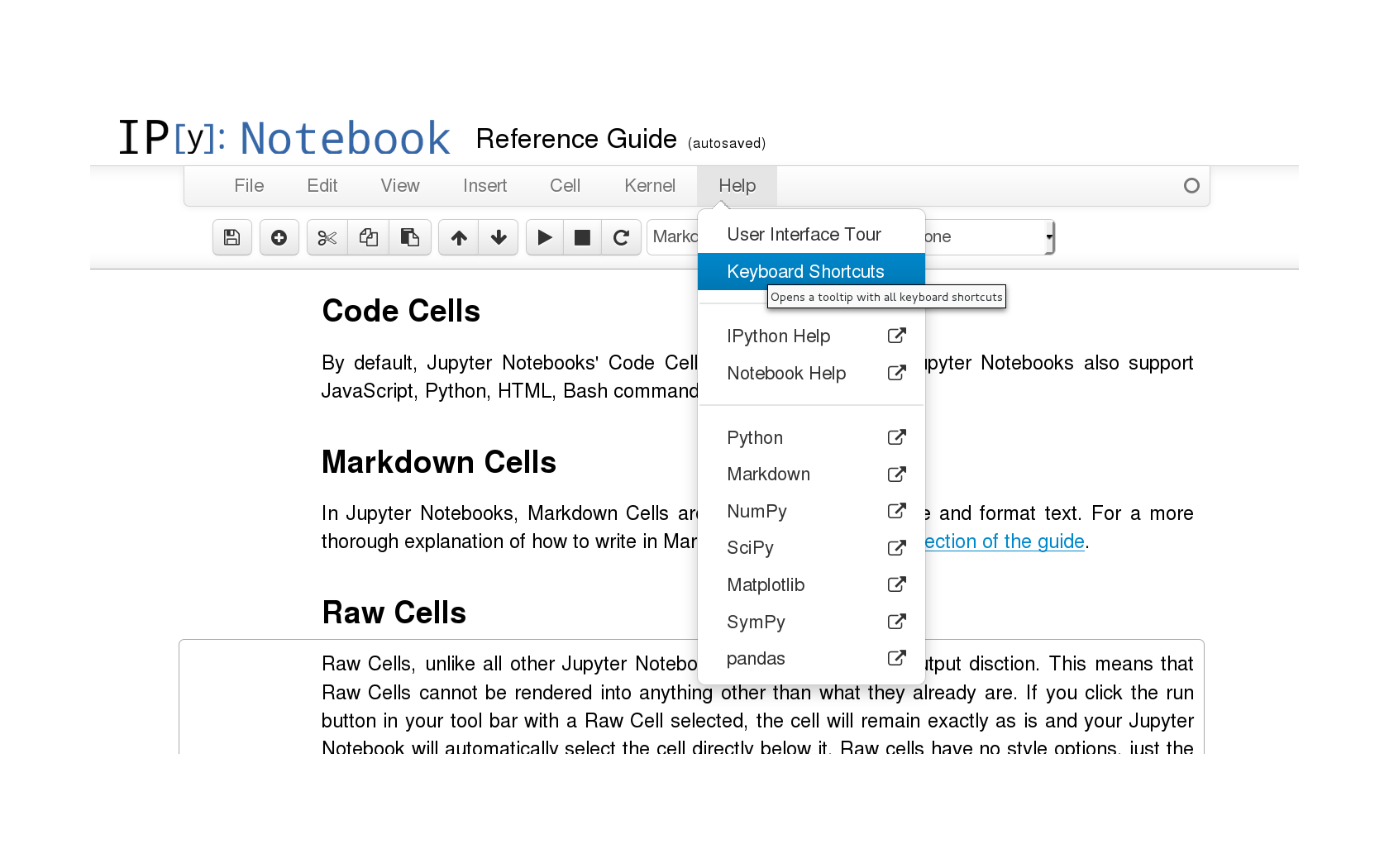
Write and execute code in a notebook’s code cell Start a Jupyter Notebooks in a specific folder via command lineĬreate a shortcut to open Jupyter Notebooks in a specific folderĮxplain the components of the Jupyter DashboardĬreate, open, rename, and delete, Jupyter Notebook documentsĮxplain what kernels are and how they are used We’ll cover the advantages (and limitations) of Jupyter Notebooks as we go, but for now, let’s dig in to the basics on how they are used.
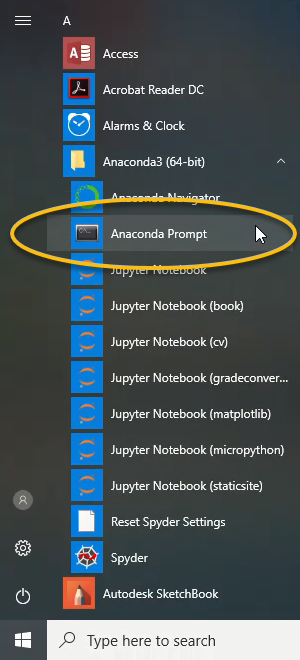
We are going to use Jupyter Notebooks and perhaps it alternative form Jupyter Lab. For now, we’re just going to select one and later come back to explore other options. There are many places to write and execute Python code. ENV 859 - Geospatial Data Analytics | Fall 2021 | Instructor: John Fay Introduction


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
